Creatine for Muscle Growth: Does it Really Work?
Creatine is one of the most widely used and researched sports supplements available today. But does this popular powder actually live up to the hype for building muscle and strength? In this article, we’ll explore what creatine is, how it works, its benefits for muscle growth, optimal ways to take it, and if it lives up to its reputation as an effective strength builder.
What is Creatine?
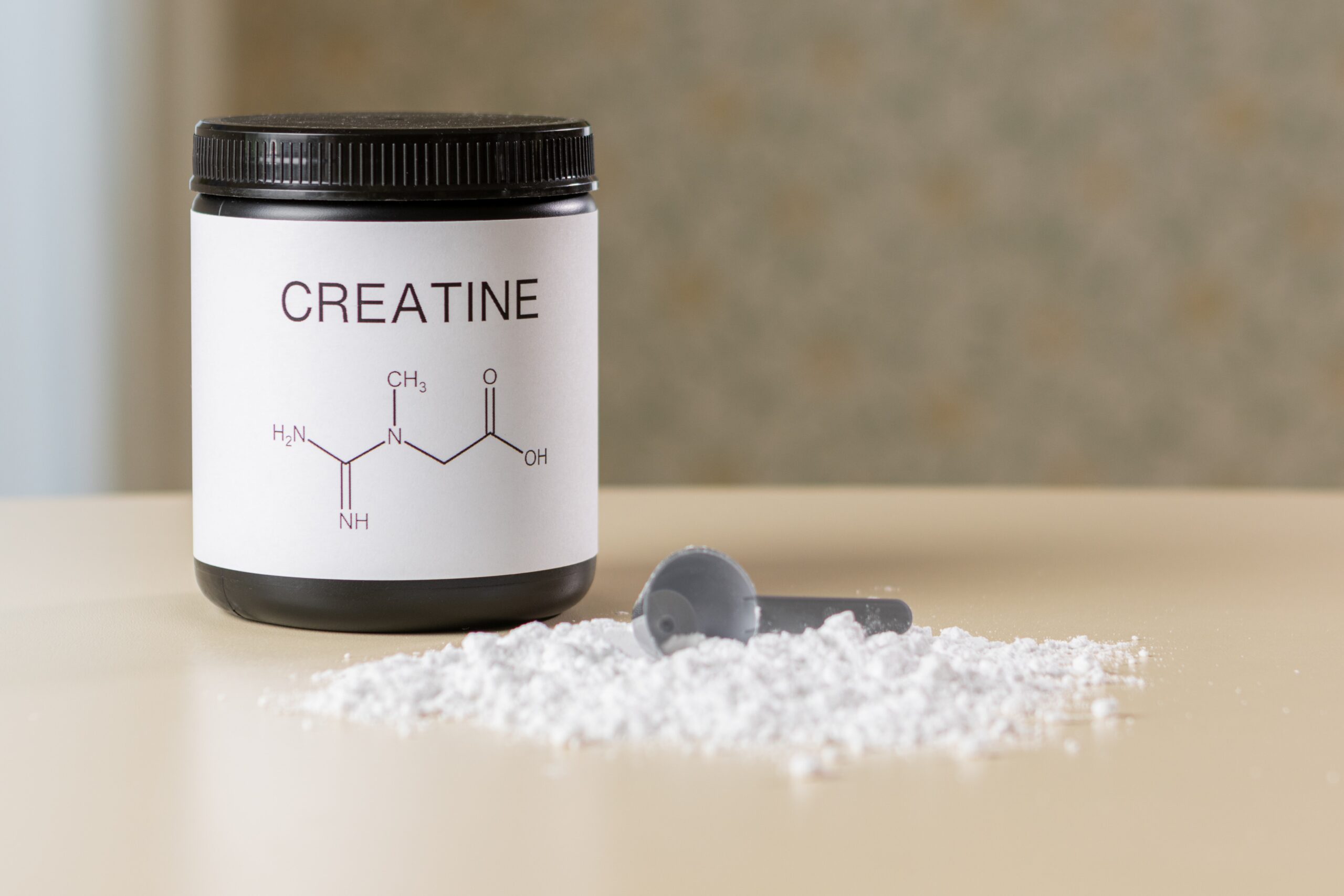
First, what exactly is creatine? Creatine is a naturally occurring compound made up of amino acids that is found in protein-rich foods such as red meat and fish. It can also be synthesized in the human body from amino acids. Inside your body, creatine is converted into phosphocreatine and stored in your muscles. Phosphocreatine donates phosphate groups to regenerate ATP, the primary energy source for high-intensity muscle contractions. In essence, creatine acts as a rapid energy buffer, allowing you to lift more weight for more reps before fatigue sets in. This is the primary mechanism behind creatine’s performance enhancing and muscle building effects. By supplementing with creatine, you can increase stores beyond what is obtained from diet and improve cellular energy production.
How Does Creatine Build Muscle?
There are several ways creatine supports greater muscle mass and strength gains:

- Increased Strength Output: By providing muscles more ATP energy, creatine allows you to lift heavier weights for additional reps before fatigue. Lifting heavier weights triggers increased protein synthesis and muscle fiber growth.
- Cell Volumization: Creatine draws more water into muscle cells, causing them to swell slightly. This puts indirect tension on the membranes, triggering anabolic signals for muscle growth.
- Higher Training Volume: The combination of increased strength, power and cell swelling allows you to do more total reps, sets and weight during a workout. This greater training volume and overload further triggers muscle growth.
- Anabolic Signaling: Research shows creatine amplifies the activation of several molecular pathways involved in muscle hypertrophy, including mTOR, satellite cell recruitment, and protein synthesis.
- Increased Protein Synthesis: By enhancing cellular energy systems, creatine improves protein synthesis rates, accelerating the rate of muscle repair and growth after training.
- Reduced Protein Breakdown: Creatine has been shown to reduce muscle breakdown rates, shifting the balance further towards more muscle accumulation.
- Increased Hormones: Studies show creatine can raise anabolic hormones like IGF-1 which are critical for facilitating muscle growth and recovery.
Benefits of Creatine for Muscle Growth
Numerous research studies conducted on creatine supplementation demonstrate significant benefits for improving muscle mass, strength and performance:
- Increases lean body mass and cross-sectional area of muscles.
- Enhances gains in 1 rep max strength.
- Improves workout performance: increased reps, lower fatigue, quicker recovery between sets.
- Increases muscle fiber size from greater training volumes.
- Decreases muscle breakdown from strenuous workouts.
A summary of over 300 research studies concluded definitively: “creatine supplementation increases strength and lean muscle mass.”
How to Take Creatine
To maximize muscle building benefits from creatine, follow these guidelines:

- Take 3-5 grams per day. Consume half before and after workouts.
- Take with a carbohydrate source – this stimulates insulin release to drive creatine into muscles.
- Take consistently for 3-4 weeks to fully saturate muscles.
- Once saturated, a maintenance dose of 3-5 grams on workout days only is sufficient.
- Take with ample water – at least 16 oz. Helps reduce side effects.
- Loading phases are unnecessary – consistent daily dose works just as well.
Creatine Considerations
Creatine is considered very safe by experts, but there are some things to keep in mind:
- Can cause water retention and temporary weight gain from cell volumization. This subsides after loading phase.
- It is important to stay well hydrated – at least 16 oz of water per 3-5 grams taken.
- Some users report mild GI side effects like cramps or diarrhea. Drinking enough water usually prevents this.
- Individuals with existing kidney conditions should not use creatine before consulting a doctor.
The Verdict: Does Creatine Work for Building Muscle?
Based on the vast body of scientific research, creatine monohydrate is clearly effective at:
- Increasing strength output, allowing you to lift heavier weights.
- Enhancing training capacity, doing more volume per workout.
- Reducing protein breakdown and muscle damage.
- Increasing protein synthesis and muscle fiber growth.
- Raising anabolic hormones and molecular signals.